Selected Publications
2021
NOX1-dependent redox signaling potentiates colonic stem cell proliferation to adapt to the intestinal microbiota by linking EGFR and TLR activation
Collaboration with Sjoerd van der Post published in Cell Reports demonstrating the key role of Nox1 in linking microbial components to epithelial stem cell proliferation.
An intercrypt subpopulation of goblet cells is essential for colonic mucus barrier function
Collaboration with Malin Johansson’s lab published in Science identifying the critical role of intercrypt goblet cells (icGCs) in maintaining colonic mucus barrier structure.
2020
Obesity-associated microbiota contributes to mucus layer defects in genetically obese mice
Collaboration with Björn Schröder’s lab at Umeå University published in JBC, identifying colonic mucus barrier defects in genetically obese mice with causal links to microbiome composition.
Perspective in Science on Kirk Bergstrom and Lijun Xia’s paper describing how mucus produced in the proximal colon contributes to distal colonic barrier function.
2019
2018
Bifidobacteria or Fiber Protects against Diet-Induced Microbiota-Mediated Colonic Mucus Deterioration
Collaboration with Fredrik Bäckhed’s and Gunnar Hansson’s labs published in Cell Host & Microbe characterizes how exposure to a low fibre, high fat diet results in a compromised colonic mucus barrier function
2016-17
Postnatal development of the small intestinal mucosa drives age-dependent, regio-selective susceptibility to Escherichia coli K1 infection
Study published in Scientific Reports showing how neuropathogenic E. coli exploit underdeveloped neonatal goblet cell-intrinsic defences to invade the small intestine
Gram-positive bacteria are held at a distance in the colon mucus by the lectin-like protein ZG16
Investigation published in PNAS characterizing the goblet cell-secreted ZG16 as a peptidoglycan-binding protein that aggregates Gram-positive bacteria and prevents them penetrating into the colonic mucus barrier
All publications
Nyström EEL, Martinez-Abad B, Arike L, Birchenough GMH, Nonnecke EB, Castillo PA, Svensson F, Bevins CL, Hansson GC, Johansson MEV. An intercrypt subpopulation of goblet cells is essential for colonic mucus barrier function. Science. 2021 Apr 16;372(6539). doi: 10.1126/science.abb1590. PubMed PMID: 33859001.
Benktander J, Padra JT, Maynard B, Birchenough G, Botwright NA, McCulloch R, Wynne JW, Sharba S, Sundell K, Sundh H, Lindén SK. Gill Mucus and Gill Mucin O-glycosylation in Healthy and Amebic Gill Disease-Affected Atlantic Salmon. Microorganisms. 2020 Nov 26;8(12). doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8121871. PubMed PMID: 33256221; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC7768351.
Birchenough GMH, Johansson MEV. Forming a mucus barrier along the colon. Science. 2020 Oct 23;370(6515):402-403. doi: 10.1126/science.abe7194. PubMed PMID: 33093095.
Schroeder BO, Birchenough GMH, Pradhan M, Nyström EEL, Henricsson M, Hansson GC, Bäckhed F. Obesity-associated microbiota contributes to mucus layer defects in genetically obese mice. J Biol Chem. 2020 Nov 13;295(46):15712-15726. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015771. Epub 2020 Sep 8. PubMed PMID: 32900852; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC7667970.
van der Post S, Jabbar KS, Birchenough G, Arike L, Akhtar N, Sjovall H, Johansson MEV, Hansson GC. Structural weakening of the colonic mucus barrier is an early event in ulcerative colitis pathogenesis. Gut. 2019 Dec;68(12):2142-2151. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317571. Epub 2019 Mar 26. PubMed PMID: 30914450; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6872445.
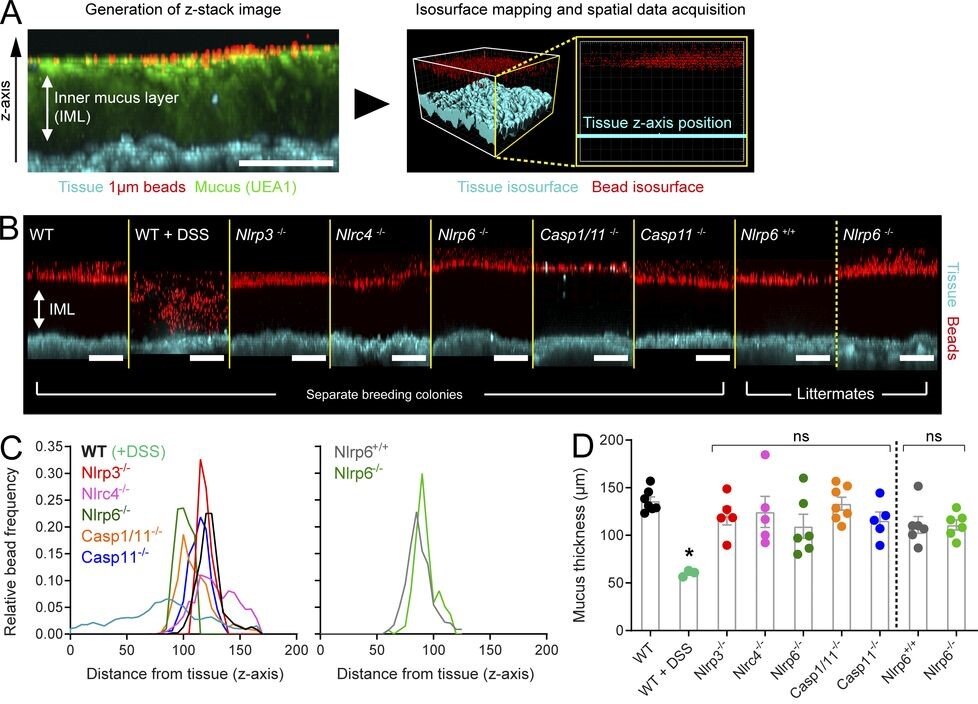
Volk JK, Nyström EEL, van der Post S, Abad BM, Schroeder BO, Johansson Å, Svensson F, Jäverfelt S, Johansson MEV, Hansson GC, Birchenough GMH. The Nlrp6 inflammasome is not required for baseline colonic inner mucus layer formation or function. J Exp Med. 2019 Nov 4;216(11):2602-2618. doi: 10.1084/jem.20190679. Epub 2019 Aug 16. PubMed PMID: 31420376; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6829596.
McCarthy AJ, Birchenough GMH, Taylor PW. Loss of Trefoil Factor 2 Sensitizes Rat Pups to Systemic Infection with the Neonatal Pathogen Escherichia coli K1. Infect Immun. 2019 Mar;87(5). doi: 10.1128/IAI.00878-18. Print 2019 Mar. PubMed PMID: 30833331; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6479038.
Birchenough G, Schroeder BO, Bäckhed F, Hansson GC. Dietary destabilisation of the balance between the microbiota and the colonic mucus barrier. Gut Microbes. 2019;10(2):246-250. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2018.1513765. Epub 2018 Sep 25. PubMed PMID: 30252606; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6546334.
Nyström EEL, Birchenough GMH, van der Post S, Arike L, Gruber AD, Hansson GC, Johansson MEV. Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Regulator 1 (CLCA1) Controls Mucus Expansion in Colon by Proteolytic Activity. EBioMedicine. 2018 Jul;33:134-143. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.05.031. Epub 2018 Jun 7. PubMed PMID: 29885864; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6085540.
Schroeder BO, Birchenough GMH, Ståhlman M, Arike L, Johansson MEV, Hansson GC, Bäckhed F. Bifidobacteria or Fiber Protects against Diet-Induced Microbiota-Mediated Colonic Mucus Deterioration. Cell Host Microbe. 2018 Jan 10;23(1):27-40.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.11.004. Epub 2017 Dec 21. PubMed PMID: 29276171; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5764785.
Birchenough G, Hansson GC. Bacteria Tell Us How to Protect Our Intestine. Cell Host Microbe. 2017 Jul 12;22(1):3-4. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.06.011. PubMed PMID: 28704650.
Bosmans JW, Jongen AC, Birchenough GM, Nyström EE, Gijbels MJ, Derikx JP, Bouvy ND, Hansson GC. Functional mucous layer and healing of proximal colonic anastomoses in an experimental model. Br J Surg. 2017 Apr;104(5):619-630. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10456. Epub 2017 Feb 13. PubMed PMID: 28195642.
Birchenough GM*, Dalgakiran F*, Witcomb LA, Johansson ME, McCarthy AJ, Hansson GC, Taylor PW. Postnatal development of the small intestinal mucosa drives age-dependent, regio-selective susceptibility to Escherichia coli K1 infection. Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 6;7(1):83. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00123-w. PubMed PMID: 28250440; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5427930. (* shared first author)
Bergström JH*, Birchenough GM*, Katona G, Schroeder BO, Schütte A, Ermund A, Johansson ME, Hansson GC. Gram-positive bacteria are held at a distance in the colon mucus by the lectin-like protein ZG16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 29;113(48):13833-13838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611400113. Epub 2016 Nov 14. PubMed PMID: 27849619; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5137749. (* shared first author)
Birchenough GM, Nyström EE, Johansson ME, Hansson GC. A sentinel goblet cell guards the colonic crypt by triggering Nlrp6-dependent Muc2 secretion. Science. 2016 Jun 24;352(6293):1535-42. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf7419. PubMed PMID: 27339979; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5148821.
Erickson NA, Nyström EE, Mundhenk L, Arike L, Glauben R, Heimesaat MM, Fischer A, Bereswill S, Birchenough GM, Gruber AD, Johansson ME. The Goblet Cell Protein Clca1 (Alias mClca3 or Gob-5) Is Not Required for Intestinal Mucus Synthesis, Structure and Barrier Function in Naive or DSS-Challenged Mice. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0131991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131991. eCollection 2015. PubMed PMID: 26162072; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4498832.
Birchenough GM, Johansson ME, Gustafsson JK, Bergström JH, Hansson GC. New developments in goblet cell mucus secretion and function. Mucosal Immunol. 2015 Jul;8(4):712-9. doi: 10.1038/mi.2015.32. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Review. PubMed PMID: 25872481; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4631840.
Dalgakiran F, Witcomb LA, McCarthy AJ, Birchenough GM, Taylor PW. Non-invasive model of neuropathogenic Escherichia coli infection in the neonatal rat. J Vis Exp. 2014 Oct 29;(92):e52018. doi: 10.3791/52018. PubMed PMID: 25408299; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4353393.
Pelaseyed T, Bergström JH, Gustafsson JK, Ermund A, Birchenough GM, Schütte A, van der Post S, Svensson F, Rodríguez-Piñeiro AM, Nyström EE, Wising C, Johansson ME, Hansson GC. The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system. Immunol Rev. 2014 Jul;260(1):8-20. doi: 10.1111/imr.12182. Review. PubMed PMID: 24942678; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4281373.
Birchenough GM, Johansson ME, Stabler RA, Dalgakiran F, Hansson GC, Wren BW, Luzio JP, Taylor PW. Altered innate defenses in the neonatal gastrointestinal tract in response to colonization by neuropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 2013 Sep;81(9):3264-75. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00268-13. Epub 2013 Jun 24. PubMed PMID: 23798529; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3754193.
Dawson LF, Valiente E, Donahue EH, Birchenough G, Wren BW. Hypervirulent Clostridium difficile PCR-ribotypes exhibit resistance to widely used disinfectants. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25754. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025754. Epub 2011 Oct 25. PubMed PMID: 22039420; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3201945.
Zelmer A, Martin MJ, Gundogdu O, Birchenough G, Lever R, Wren BW, Luzio JP, Taylor PW. Administration of capsule-selective endosialidase E minimizes upregulation of organ gene expression induced by experimental systemic infection with Escherichia coli K1. Microbiology. 2010 Jul;156(Pt 7):2205-2215. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.036145-0. Epub 2010 Apr 15. PubMed PMID: 20395269; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2923034.